Worksheet 5 double replacement reactions – Worksheet 5: Double Replacement Reactions delves into the captivating realm of chemical reactions, where elements and compounds engage in a dynamic dance of exchange. This exploration unveils the fundamental concepts, prediction methods, and diverse applications of double replacement reactions, providing a comprehensive understanding of this intriguing chemical phenomenon.
Double Replacement Reactions: Concepts: Worksheet 5 Double Replacement Reactions
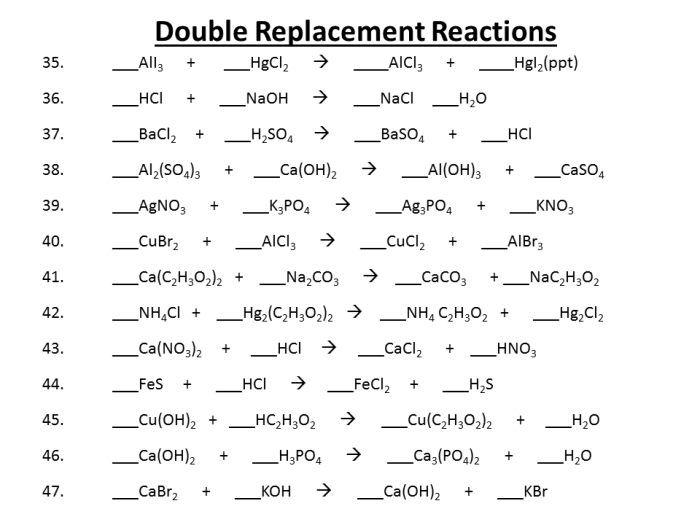
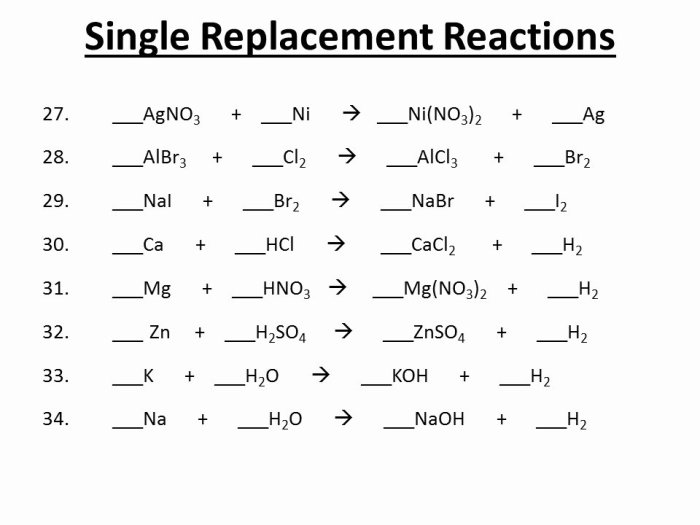
Double replacement reactions are a type of chemical reaction in which two ionic compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds. These reactions are also known as double displacement reactions or metathesis reactions. The general equation for a double replacement reaction is:AB + CD → AD + CBFor example, when sodium chloride (NaCl) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) are mixed, they react to form sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and silver chloride (AgCl).
The reaction equation is:NaCl + AgNO3 → NaNO3 + AgClDouble replacement reactions occur when the following conditions are met:* The reactants are ionic compounds.
- The ions in the reactants are oppositely charged.
- The products are also ionic compounds.
Predicting Products of Double Replacement Reactions
The activity series of metals is a list of metals arranged in order of their reactivity. Metals higher on the list are more reactive than metals lower on the list. When a metal higher on the list reacts with a metal lower on the list, the more reactive metal will replace the less reactive metal in the compound.The
solubility guidelines are a set of rules that can be used to predict whether a compound is soluble in water. A compound is soluble in water if it dissolves to form a clear solution. If a compound does not dissolve to form a clear solution, it is insoluble.The
solubility guidelines can be used to predict the products of a double replacement reaction. If the products of the reaction are both soluble, the reaction will occur. If one or both of the products are insoluble, the reaction will not occur.
Types of Double Replacement Reactions
There are three main types of double replacement reactions: precipitation reactions, acid-base reactions, and gas-forming reactions.*
- *Precipitation reactions are reactions in which one of the products is a solid that precipitates out of solution.
- *Acid-base reactions are reactions in which one of the products is an acid or a base.
- *Gas-forming reactions are reactions in which one of the products is a gas.
Applications of Double Replacement Reactions, Worksheet 5 double replacement reactions
Double replacement reactions are used in a variety of applications, including:*
- *Water treatment
- Double replacement reactions can be used to remove impurities from water. For example, lime (CaO) is added to water to remove calcium ions (Ca2+). The calcium ions react with the lime to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3), which precipitates out of solution.
- *Medicine
- Double replacement reactions are used to make a variety of medicines. For example, antacids are used to neutralize stomach acid. Antacids contain compounds such as calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide, which react with stomach acid to form water and carbon dioxide.
- *Industry
- Double replacement reactions are used in a variety of industrial processes. For example, double replacement reactions are used to make glass, paper, and fertilizers.
Clarifying Questions
What are the necessary conditions for a double replacement reaction to occur?
Double replacement reactions require the presence of two ionic compounds in an aqueous solution, with the cations and anions of the reactants exchanging places to form new compounds.
How can we predict the products of a double replacement reaction?
The activity series of metals and the solubility guidelines provide valuable tools for predicting the products of double replacement reactions. The more reactive metal will replace the less reactive metal, and the more soluble compound will form.
What are the different types of double replacement reactions?
Double replacement reactions can be classified into three main types: precipitation reactions, acid-base reactions, and gas-forming reactions. Each type exhibits distinct characteristics and has unique applications.